Wormwood: A bitter herb with incredible healing potential
07/23/2025 / By Ava Grace
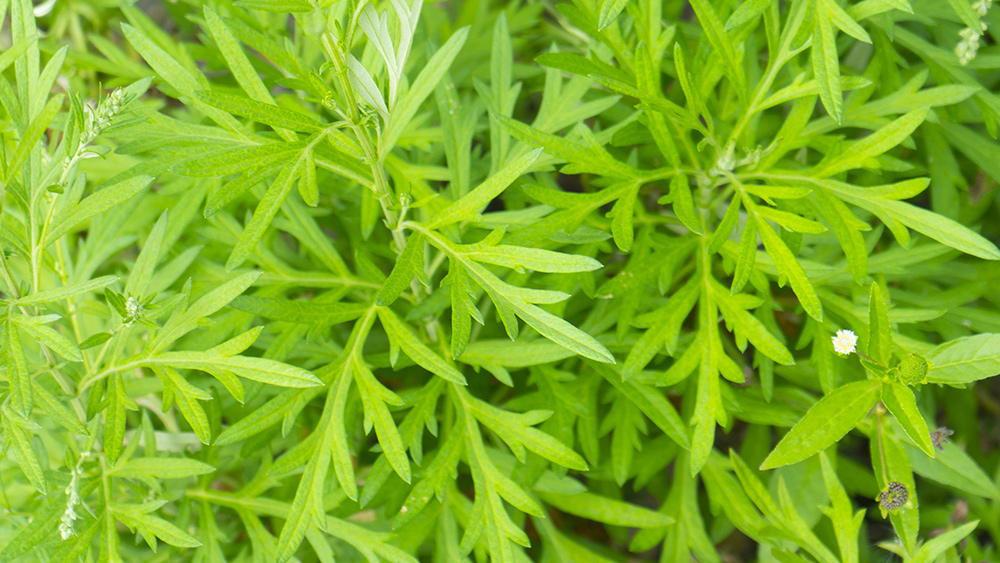

- Artemisia absinthium, or wormwood, is a perennial plant native to North Africa and Eurasia, known for its silvery-green foliage, bitter taste, and strong aroma. It has historical significance in traditional medicine, culinary arts, and folklore, particularly for its role in producing absinthe.
- Wormwood is valued for its digestive, antiparasitic, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. It supports liver function, aids in expelling intestinal parasites, and may enhance mental clarity and mood when used moderately.
- Used in Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine, and European herbalism, wormwood is consumed as tea, tinctures, or capsules. It is also used in culinary traditions, such as Moroccan teas and European spirits like absinthe and vermouth.
- While its bitterness limits its use in everyday cooking, wormwood can be incorporated into teas, infused honey, herbal bitters and homemade vermouth for those who appreciate its unique flavor and health benefits.
- Wormwood contains thujone, which can be toxic in large doses. It is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, individuals with epilepsy, or those with kidney disorders. Consultation with a healthcare professional is advised before use.
Artemisia absinthium, commonly known as wormwood, is a herbaceous perennial plant with a storied history, known for its medicinal properties and its role in the production of absinthe, the infamous green spirit. Native to North Africa and temperate regions of Eurasia, wormwood has been naturalized in parts of Canada and the northern United States. Its silvery-green foliage, bitter flavor and potent aroma have made it a staple in traditional medicine, culinary arts and even folklore.
Wormwood is known by a variety of names, reflecting its widespread use and cultural significance. It is often referred to as common wormwood, absinthe wormwood or simply absinthe. In some regions, it is also called “green ginger” or “old woman,” the latter likely a reference to its use as a traditional medicine for women. The name “wormwood” is thought to have come from its traditional use as a remedy for intestinal worms — a testament to its potent antiparasitic properties. (Related: Wormwood: An ancient cleanser and detoxifier.)
Wormwood is easily recognizable by its silvery-green leaves, which are finely divided and covered in tiny, hair-like structures that give the plant a soft, almost velvety texture. The leaves grow in a bushy, upright manner, and the plant produces small, yellow-green flowers in late summer. The aroma of wormwood is intensely herbal, with a sharp, camphor-like scent that can be both invigorating and overwhelming.
The taste of wormwood is famously bitter, often described as one of the most bitter herbs in the plant kingdom. This bitterness is due to the presence of compounds like absinthin and anabsinthin, which are also responsible for many of wormwood’s therapeutic effects. While its bitterness can be off-putting for some, it is precisely this quality that makes wormwood a valuable digestive aid and a key ingredient in traditional herbal remedies.
Health benefits of wormwood
Wormwood has been used for centuries in traditional medicine systems, including Ayurveda, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and European herbalism. Modern research has validated many of wormwood’s medicinal uses, shedding light on its potential to prevent or alleviate a variety of health conditions.
Here are some of wormwood’s most notable benefits:
- Digestive health – Wormwood is perhaps best known for its ability to stimulate digestion. Its bitter compounds trigger the production of digestive enzymes and bile, aiding in the breakdown of food and the absorption of nutrients. This makes it particularly useful for individuals suffering from indigestion, bloating, or loss of appetite.
- Antiparasitic properties – As its name suggests, wormwood has long been used to expel intestinal parasites. The compound thujone, found in wormwood, is believed to be responsible for its antiparasitic effects. It is often combined with other herbs like black walnut and cloves in natural parasite cleanse protocols.
- Anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects – Wormwood contains several bioactive compounds, including flavonoids and essential oils, that exhibit anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. These properties make it a potential ally in combating infections and reducing inflammation in conditions like arthritis.
- Liver support – Wormwood is considered a liver tonic in many traditional medicine systems. It is believed to support liver function by promoting detoxification and protecting liver cells from damage.
- Mental clarity and mood – Historically, wormwood was used to enhance mental clarity and uplift the spirit. While its role in absinthe has given it a reputation for inducing hallucinations, moderate and controlled use of wormwood in herbal preparations is thought to have a calming and focusing effect on the mind.
For medicinal purposes, wormwood is typically consumed as a tea, tincture or capsule. Anecdotal evidence suggests that wormwood tea, when consumed in moderation, can help alleviate digestive discomfort and boost energy levels. However, due to its potency, it is important to use wormwood under the guidance of a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider.
Culinary uses
Wormwood is not commonly used in everyday cooking due to its intense bitterness, but it has found its niche in certain culinary traditions. In Morocco, for example, wormwood is used to flavor teas and infusions, often combined with mint and sugar to balance its bitterness. In Europe, it is a key ingredient in absinthe and vermouth, with its flavor often celebrated and moderated by other botanicals.
While wormwood is not a mainstream culinary herb, it can be incorporated into recipes that showcase its unique flavor and health benefits. Here are a few creative ideas:
- Wormwood digestive tea – Steep a teaspoon of dried wormwood leaves in hot water for 5-10 minutes. Add honey or lemon to balance the bitterness.
- Wormwood-infused honey – Combine dried wormwood with raw honey and let it infuse for several weeks. Use this honey to sweeten teas or drizzle over yogurt.
- Herbal bitters with wormwood – Create a homemade digestive bitters blend using wormwood, gentian root, orange peel, and other bitter herbs.
- Wormwood vermouth – Infuse white wine with wormwood, juniper berries, and citrus peel to create a homemade vermouth.
While wormwood offers numerous health benefits, it is important to use it responsibly. The compound thujone, while beneficial in small amounts, can be toxic in large doses. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as individuals with epilepsy or kidney disorders, should avoid wormwood. Always consult a healthcare professional before incorporating wormwood into your wellness routine.
Wormwood is a fascinating herb with a rich history and a wide range of potential health benefits. From its role in digestive health to its antiparasitic and anti-inflammatory properties, this bitter herb has much to offer. While its intense flavor may not appeal to everyone, its therapeutic potential makes it a valuable addition to the world of herbal medicine. Whether enjoyed as a tea, infused into honey or used in homemade bitters, wormwood is a testament to the healing power of nature.
This story is not medical advice and is not intended to treat or cure any disease. Always consult with a qualified naturopathic physician for personalized advice about your specific health situation or concern.
Visit NaturalNews.com, a great article source where you can learn about superfoods and their health benefits.
You can also try Brighteon.ai, an AI model created by Mike Adams, also known as the Health Ranger. This model is available as a free download to be run locally and is designed to help share and decentralize knowledge. By doing so, it aims to bypass censorship and empower people with knowledge.
If you’re looking for an uncensored video free speech website where you can openly discuss nutrition, natural medicine, ingredients and more, check out Brighteon.com and these two free speech social media sites, Brighteon.IO and Brighteon.social.
This video is from the HealthPetal channel on Brighteon.com.
More related stories:
Wormwood: Bitter herb with potent medicinal properties.
Wormwood is a natural remedy for treating intestinal parasites.
Artemisinin from sweet wormwood treats not just malaria but also CANCER.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, food cures, food is medicine, food science, functional food, healing, health science, herbal medicine, Herbs, ingredients, natural cures, natural health, natural medicine, Naturopathy, organics, phytonutrients, plant medicine, remedies, wormwood
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
HealthScience.News is a fact-based public education website published by Health Science News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Health Science News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.