Vitamin C: An essential nutrient for good overall health
07/06/2022 / By Olivia Cook

Vitamin C, medically known as ascorbic acid, is an essential water-soluble nutrient synthesized in plants. It was discovered by a Hungarian biochemist, Albert Szent-Gyorgyi, who was investigating a life-threatening disease called scurvy that was prevalent in sailors in the early 1930s.
It was later found that vitamin C enables the body to efficiently use carbohydrates, healthy fats and proteins by improving absorption.
Vitamin C supports the growth and health of bones, teeth, gums, ligaments and blood vessels because it acts as an antioxidant that chemically binds and neutralizes harmful free radicals. Vitamin C also plays a key role in the formation of collagen – the body’s major protein-builder – and is therefore essential to the proper functioning of all internal organs like your brain, heart, lungs, liver, bladder, kidneys, stomach and intestines.
Health benefits of vitamin C
Here are some of vitamin C’s health benefits and the science behind them.
Supports a healthy immune system
According to a study published in the journal Nutrients, vitamin C contributes to immune defense by supporting various cellular functions of both the innate and adaptive immune systems. This essential micronutrient also supports the barrier function of epithelial cells that line the surfaces of your body against pathogens or infectious agents and promotes the oxidant scavenging activity of the skin.
Supports cognitive health
A study that appeared in the journal Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience showed that vitamin C is crucial to cognitive performance. It plays a role in the differentiation and maturation of nerve cells that are fundamental units of the brain and nervous system and in the formation of the insulating layer that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord (myelin sheath), that protects neurons and speeds up impulse transmission.
In conclusion, there is a significant association between vitamin C concentrations and performance on tasks involving attention, focus, working memory, decision speed, delayed and total recall and recognition.
Supports cardiovascular health
A study that appeared in the journal International Journal of Molecular Sciences concluded that vitamin C plays a pivotal role in preventing the pathogenesis of cardiac and vascular disorders, including coronary heart disease, heart failure, hypertension and cerebrovascular diseases. Vitamin C’s importance lies in its antioxidant activity, which is crucial for protecting against oxidative stress and chronic inflammation. (Related: Vitamin C could reduce risk of stroke.)
Supports respiratory health
In a study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, researchers from the University of Nottingham reported that vitamin C can help protect the lungs by reducing the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), an inflammatory lung disease.
Supports a healthy digestive system
Getting insufficient amounts of vitamin C from your diet reduces your stomach’s production of hydrochloric acid, which is needed to digest and break down food. This may leave you with digestive issues like burping, farting and heartburn. You can improve your digestion by simply getting enough vitamin C.
A study published in the journal Redox Biology associates poor vitamin C status with metabolic syndrome (MetS), a cluster of conditions that raises your cardiometabolic risk factors and endotoxemia, or the presence of endotoxins in the blood. If derived from gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria, these endotoxins may cause hemorrhages, necrosis of the kidneys and shock. Endotoxins are released when bacteria die, and dissociated endotoxins are able to cross the gastrointestinal barrier and enter your bloodstream.
Supports skin health
A study published in the journal Nutrients showed that vitamin C supports important functions, including stimulating collagen synthesis and assisting in antioxidant protection against UV-induced photodamage and other harmful stuff from the environment, including air pollution. Over time, the buildup of free radicals is greatly responsible for signs of premature aging, among others. (Related: A simple and natural facemask with vitamin C)
Supports oral health
A study that appeared in the Journal of the Canadian Dental Association showed that vitamin C’s role in maintaining the health of teeth and gums remains unchallenged. Current clinical evidence indicates that vitamin C helps improve host defense mechanisms and is important for preserving periodontal health.
Naturally elevates your mood
A study that appeared in the journal Antioxidants (Basel) associated high vitamin C status with elevated mood in a sample of 139 young adult male tertiary students aged 18 to 25 years.
One of the best-established functions of vitamin C is in the regulation of neurotransmitter biosynthesis, including that of catecholamines (hormones that the brain, nerve tissues and adrenal glands produce), which are responsible for your body’s “fight-or-flight” response.
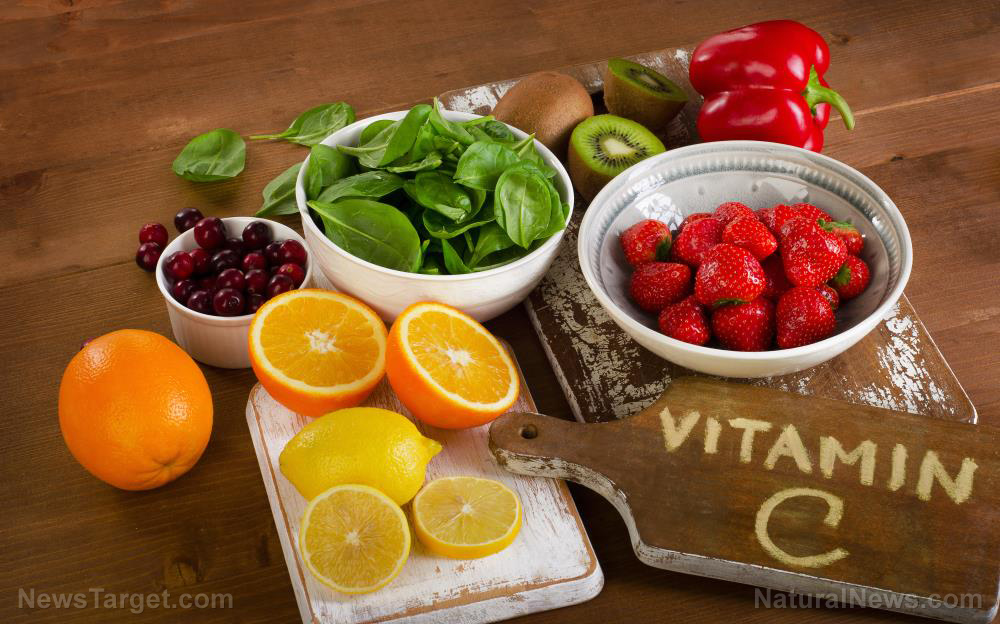
If you’re looking to get vitamin C, eat organic and whole fruits with their accompanying fiber and pulp. They provide many key nutrients and antioxidants, including vitamin C. Vegetables such as broccoli, Brussel sprouts, cauliflower, spinach and other leafy greens are also rich sources of vitamin C.
Watch the video below that talks about the benefits of vitamin C.
This video is from the Holistic Herbalist channel at Brighteon.com.
More related stories:
Vitamin C outperforms vaccines.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
aging secrets, anti-aging, antioxidant, ascorbic acid, brain health, digestive health, food science, health science, heart health, immune system, mental health, natural health, nutrients, oral health, respiratory health, skin health, supplements, vitamin C
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
HealthScience.News is a fact-based public education website published by Health Science News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Health Science News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.